Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) are pursuing a completely new and unconventional strategy to improve the way data can be processed and – in particular – stored. The team members, based in Mainz and Jerusalem, have come up with the idea of bringing together two different forms of chirality to develop new data storage systems that are faster, smaller, and more efficient than those currently available.
Chirality, also known as handedness in this context, describes objects that come in two distinctly different configurations that are mirror images of each other such as our left and right hand. “We were inspired by nature, where chirality is a common phenomenon. Chiral molecules can act like a filter for electron spin and ensure functionality even on the smallest scale,” said Professor Angela Wittmann of the JGU Institute of Physics.
Combining the chirality of spin configurations and molecules
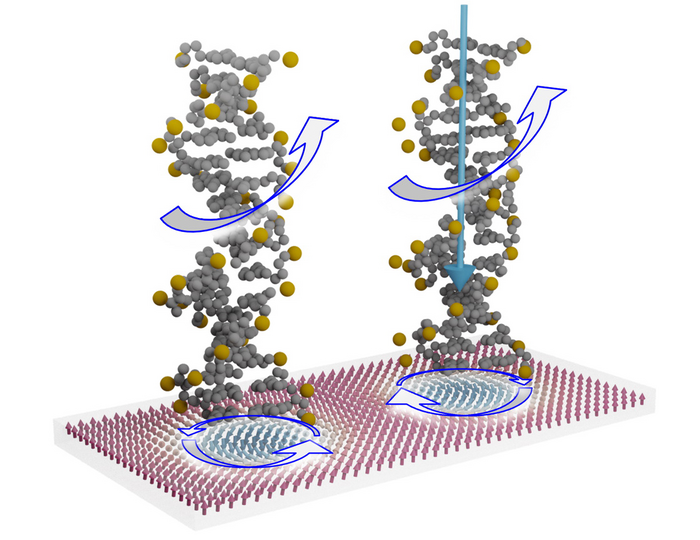
In their approach, the researchers from the fields of experimental solid state physics, atomic physics, and molecular chemistry will be using recently discovered chiral spin structures. These so-called skyrmions are tiny vortices in magnetic thin films protected by their chirality. It is this kind of chiral magnetic texture that the researchers intend to combine with chiral molecules over the course of the project. The assumption is that, based on the chiral-chiral interaction, they would have a unique, flexible, controllable, and efficient means of manipulating spin structures. “With the help of a chiral molecule, it should be possible to switch the handedness of the chiral magnetic textures in thin films, for instance, from clockwise to anticlockwise,” clarified Wittmann.
Two chiral molecules on chiral spin structures in a magnetic thin film/Two chiral molecules on chiral spin structures in a magnetic thin film (ill./©: Angela Wittmann)
In this case, the chiral molecule with its DNA-like helix structure would act like a spin filter, allowing only certain electrons moving in one direction to pass while holding others back. The researchers will use highly sophisticated sensor technologies to determine how and whether this interaction actually works.
“Our project is groundbreaking in that it brings together two different types of chirality,” emphasized Wittmann. According to the researchers, there is a very real chance that their innovative concept involving the utilization of spintronic components will result in the creation of the next generation of innovative storage, logic, and sensor devices that could be employed in unconventional computing.
The consortium consists of four members of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and two members of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, who will be contributing their expertise in various disciplines. At JGU, these are Professor Angela Wittmann and Professor Mathias Kläui of the Condensed Matter Physics group, Professor Dmitry Budker of the Quantum, Atomic, and Neutron Physics group and the Helmholtz Institute Mainz (HIM), and Professor Eva Rentschler of the Department of Chemistry, collaborating with their partners Professor Yossi Paltiel and Professor Nir Bar-Gill of the Department of Applied Physics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
Carl Zeiss Foundation sponsoring innovative projects through its new CZS Wildcard program
In early 2022, the Carl Zeiss Foundation launched its CZS Wildcard program with the objective of promoting unconventional, interdisciplinary research in the STEM field. Each team must consist of at least three researchers. The purpose of the program is to support projects that are still in a very early phase of realization and are built on original and unconventional concepts with a high potential for innovation. The first five teams will be starting work in early 2023
Also Read:
Detecting Alzheimer’s disease in the blood using Digital ICA
Turning fish waste into quality carbon-based nanomaterial
https://indiainternationaltimes.com/imagine-world-map-without-humans-here-it-is/37