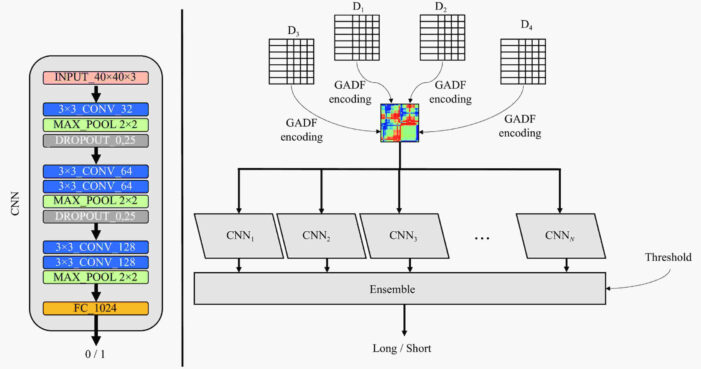
Using the science of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with deep learning – a discipline within artificial intelligence, Italian researchers have developed a system of market forecasting with the potential for greater gains and fewer losses than previous attempts to use AI methods to manage stock portfolios.
The team, led by Prof. Silvio Barra t the University of Cagliari, published its findings in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica. The University of Cagliari-based team set out to create an AI-managed “buy and hold” (B&H) strategy – a system of deciding whether to take one of three possible actions – a long action (buying a stock and selling it before the market closes), a short action (selling a stock, then buying it back before the market closes), and a hold (deciding not to invest in a stock that day).
At the heart of their proposed system is an automated cycle of analyzing layered images generated from current and past market data unlike the older B&H systems, based on machine learning, a discipline that leans heavily on predictions based on past performance.
Just like seasoned investor
By letting their proposed network analyze current data layered over past data, they are able to take market forecasting a step further, allowing for a type of learning that more closely mirrors the intuition of a seasoned investor rather than a robot. Their proposed network can adjust its buy/sell thresholds based on what is happening both in real time and the past. Taking into account present-day factors increases the yield over both random guessing and trading algorithms not capable of real-time learning, they said.
To train their CNN for the experiment, the research team used S&P 500 data from 2009 to 2016. The S&P 500 is widely regarded as a litmus test for the health of the overall global market.
At first, their proposed trading system predicted the market with about 50 percent accuracy, or about accurate enough to break even in a real-world situation. They discovered that short-term outliers, which unexpectedly over- or underperformed, generating a factor they called “randomness.” Realizing this, they added threshold controls, which ended up greatly stabilizing their method.
“The mitigation of randomness yields two simple, but significant consequences,” Prof. Barra said. “When we lose, we tend to lose very little, and when we win, we tend to win considerably.” Howwever, further enhancements will be needed, said Prof. Barra, as other methods of automated trading already in use make markets more and more difficult to predict.